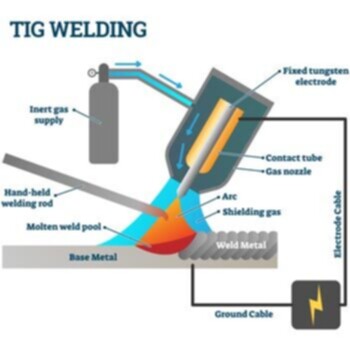
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG)
Welding together thick sections of stainless steel or non-ferrous metals is the most common use for this method. It is an arc-welding process that uses a fixed consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. This process is much more time consuming than MIG, Stick or Flux Cored Arc Welding.
The melting point of non-ferrous metals vary considerably, so care must be taken in identifying the composition of the base metal. Stainless Steel and Steel both contain Iron, however, to be considered Stainless Steel, the metal must contain at least 11% Chromium. Carbon Steel melts in the 2,600 to 2,800-degree F range.
The presence of 11% chromium in stainless steel narrows that temperature range to the 2,750+/- degree F mark. But nothing shows welding skills more than the intricate ability to TIG weld aluminum. This skill takes a steady hand, trained eye, and an artistic touch to create a smooth, amazing weld.

